This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Screw conveyors and grit classifiers
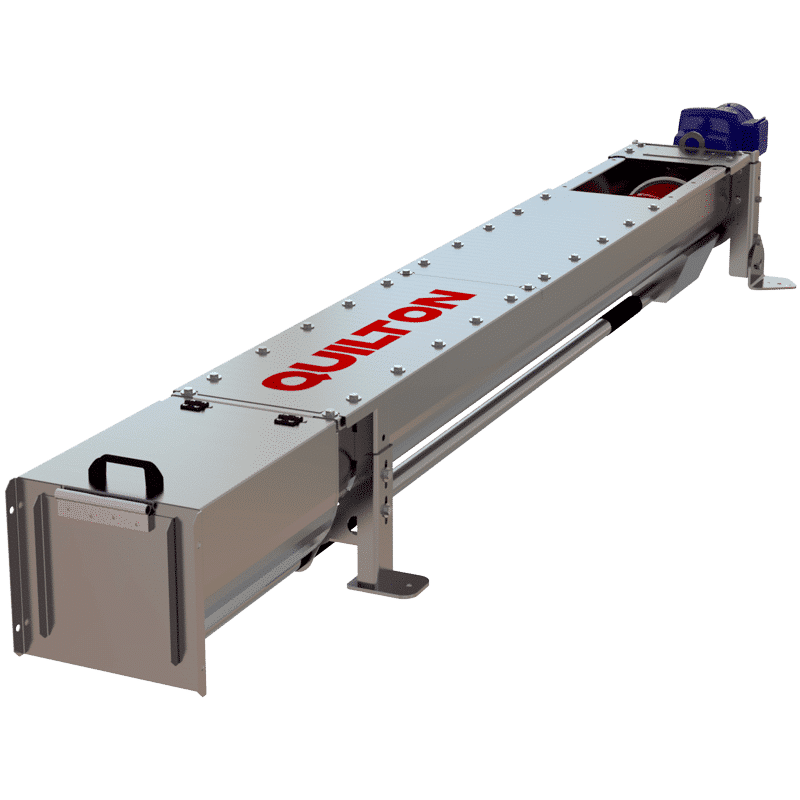
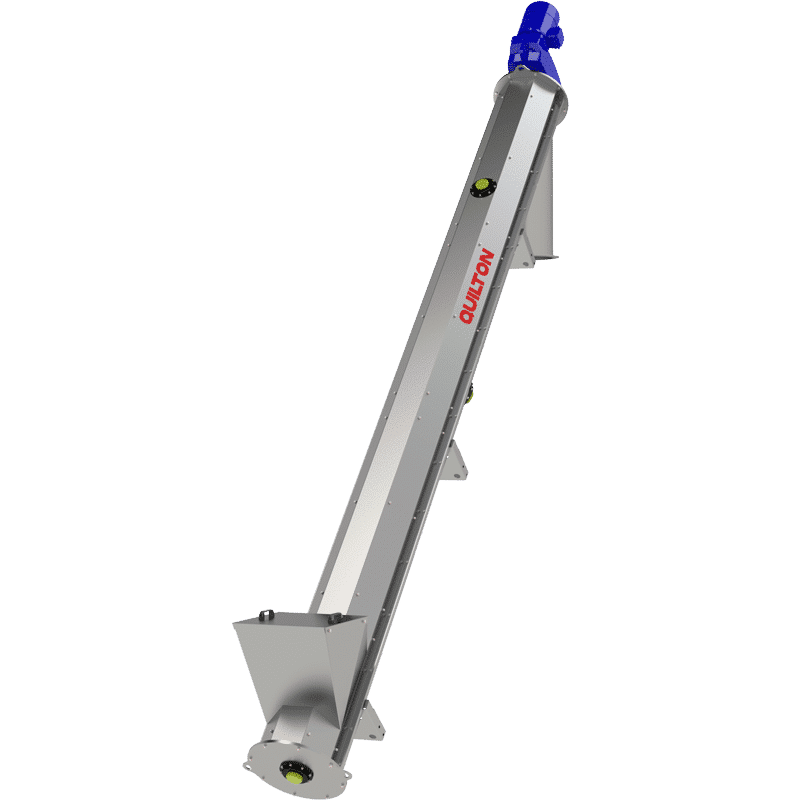
QUILTON pioneered the launch in Spain of the concept of a shaftless auger for moving solids in water treatment plants. Screw conveyors provide sundry options for collecting and removing wastes from roughing, desanding and desilting, and the movement of sludges, being used to transport difficult products, such as wet materials, sludges, and irregular-shaped and fibrous particles, which tend to form plugs or clog together.
In turn, grit classifiers are used to separate sands and heavy sediments in the mixture of grit and water removed from desanders.
QUILTON provides a range of solutions to cater for each customer’s requirements, for the collection and removal of wastes from the pre-treatment, desanding and movement of sludges, in all those cases in which hygienic conditions need to be, and indeed must be, upheld.
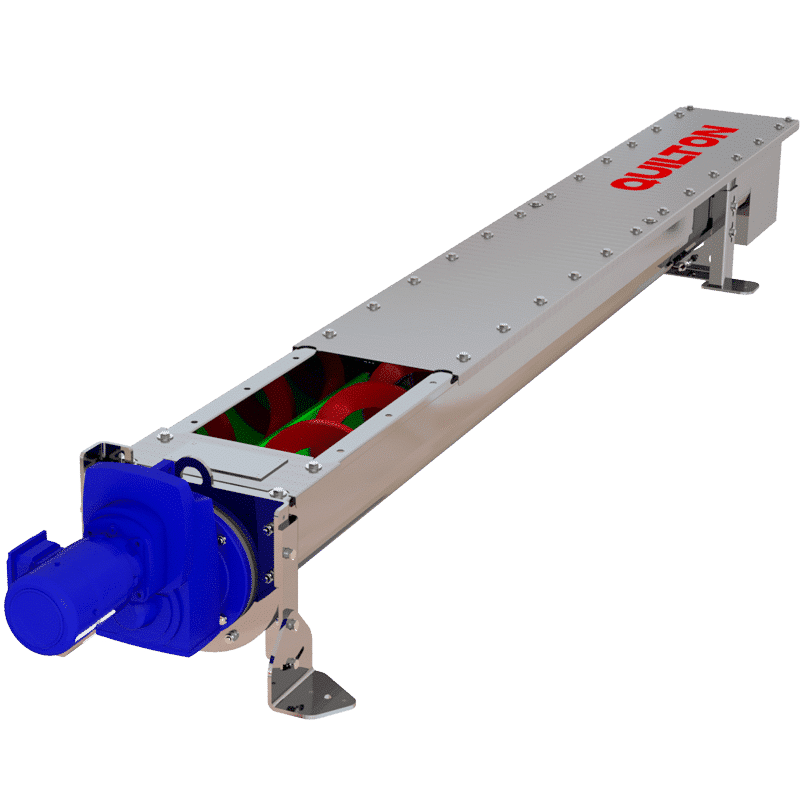
QUILTON SCREW CONVEYORS AND GRIT CLASSIFIERS
Other product families
Mostrando 5 resultados
GRIT CLASSIFIERS AND CONVEYORS. DESCRIPTION AND USE
The volume of waste retained by the roughing process (bar screens and screens) varies significantly from one treatment station to another, depending largely on the amount of waste, the type of bar screen or screen, the gap between the round or flat bars, the flow of wastewater, the type of drains, the installation’s geographical location, and the specific nature of each community. These wastes vary considerably in composition depending on the nature of the urban and industrial effluents.
The design and operation of these pieces of equipment involve a robust screw or spiral with no central shaft and made of thick stainless steel. The screw or spiral is reinforced in some cases to increase its strength and its conveyor capacity.
SCREW CONVEYORS
The waste collected in the roughing process is normally removed by an arrangement of conveyor belts or augers for its disposal in a hopper or skip. Screw conveyors tend to have a start-up system for synchronising their operation with the bar screen, screen, or machinery of origin.
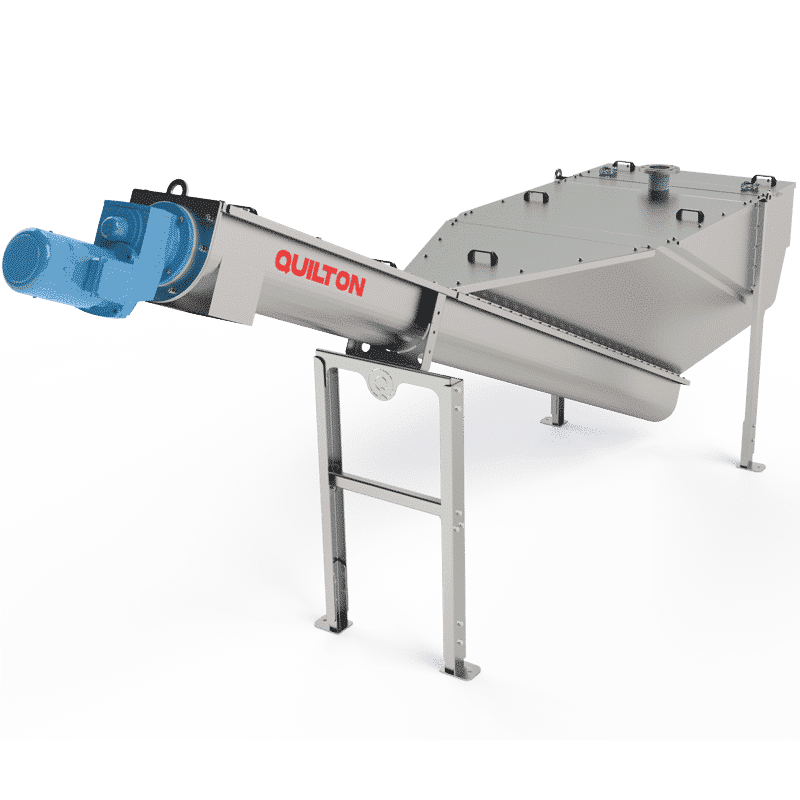
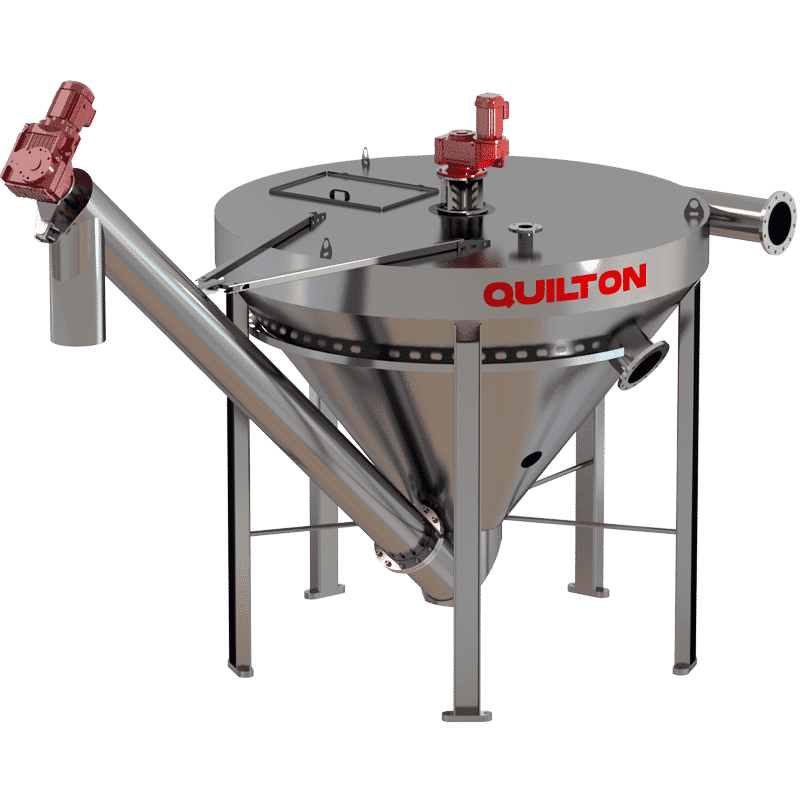
GRIT CLASSIFIERS
The desanding process is used to remove heavy particles of more than 200 micra in order to avoid sediments in the channels and conduits, protect the pumps and other devices against abrasion, and avoid overloads in subsequent processing stages.
The volume of grit removed from the desanders varies considerably depending on the water collection system, the state of the drains, weather conditions, type of effluent, etc., with this being a highly important aspect to consider prior to the design of the pre-treatment.
The grit-water mixture from the desanders may be decanted in different ways: sedimentation in shallow tanks, mechanical separation, the use of hydrocyclones and storage in a hopper with an overflow chute or hydrocyclone and collection by an Archimedes screw prior to storage.
QUILTON has classifying equipment for grit washing that provides a joint solution for decanting grit from the mixture in the desanding process and its subsequent washing.